Botanical Information
- Scientific Name: Solanum macrocarpon
- Common Names: Gboma eggplant, African eggplant, Garden egg, Mock to
- Origin: Indigenous to tropical Africa, specifically West and Central regions
Plant Description
- Leaves: Large, broad, and dark green, similar in appearance to spinach or kale. They are the primary part used as a leafy vegetable.
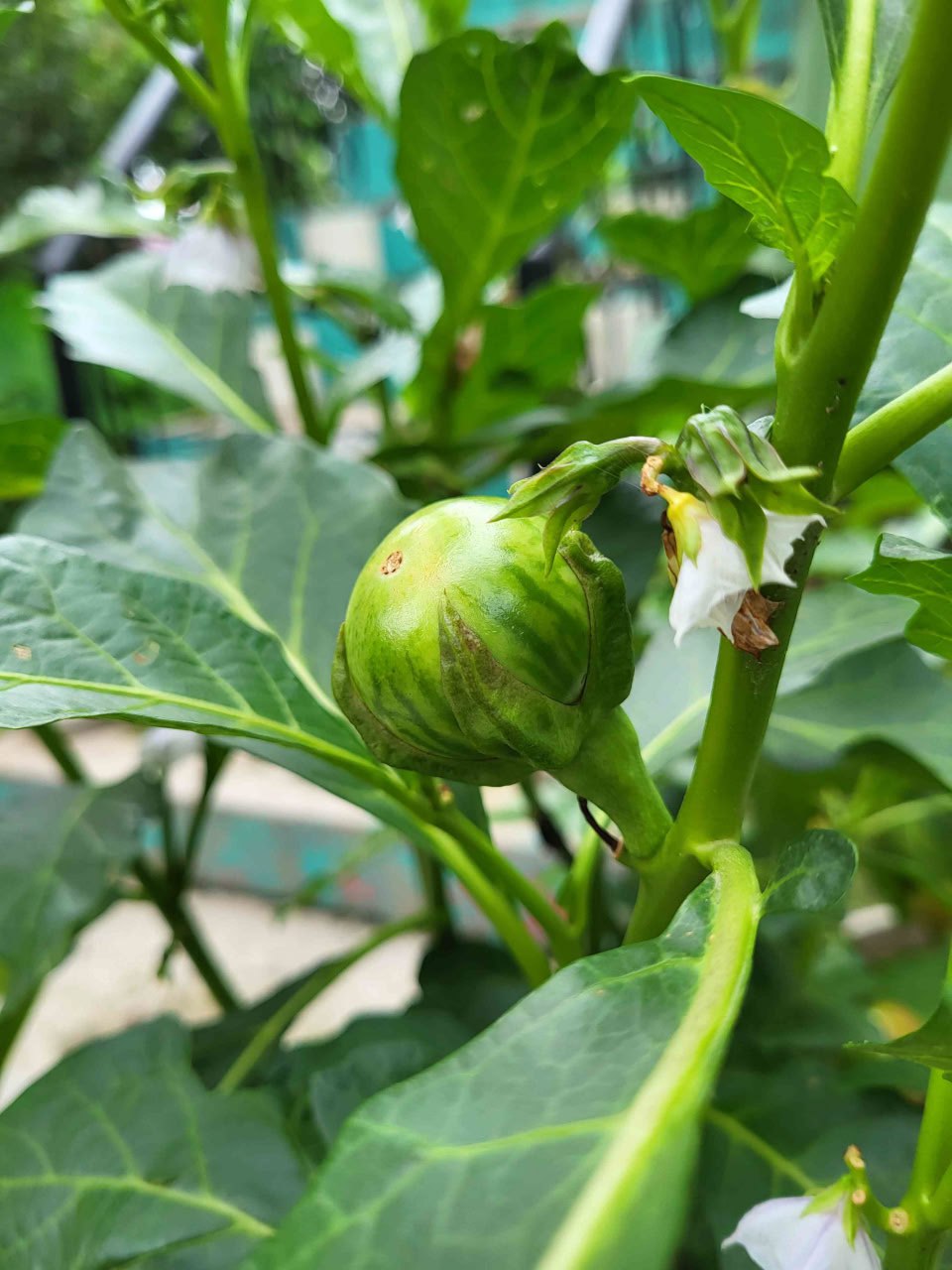
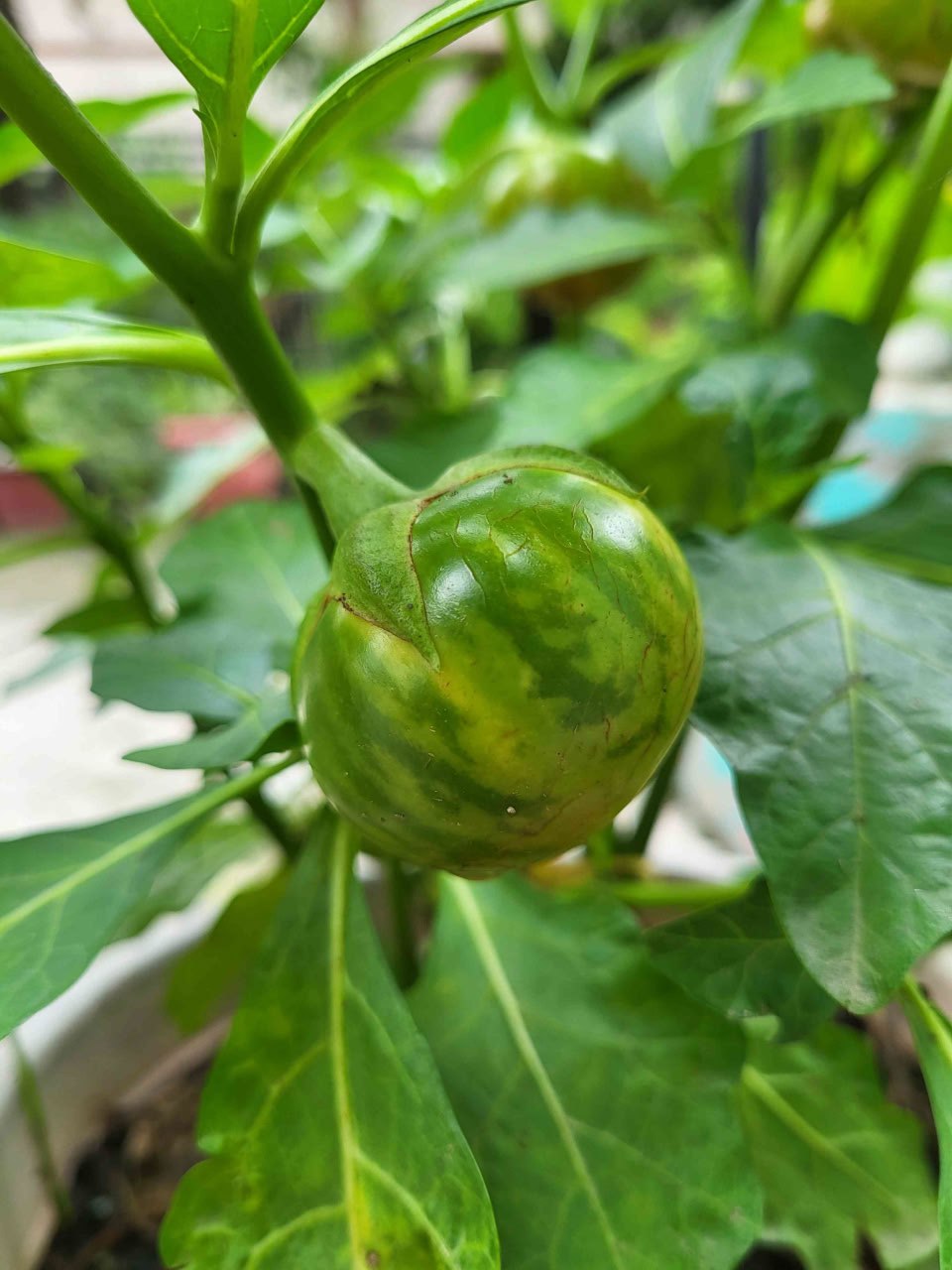
- Fruits: Small, round or oval, and resemble miniature eggplants. They can vary in color from green to white, yellow, or purple. The fruits are slightly bitter but become more palatable when cooked.
- Growth: The plant is hardy and can thrive in tropical climates. It tolerates drought conditions well, making it suitable for areas with variable rainfall.
Health Benefits
- Nutrient-rich: Gboma leaves provide a good source of vitamins and minerals that contribute to bone health, immune function, and overall well-being.
- Antioxidants: The leaves and fruits contain antioxidants that help reduce oxidative stress in the body.
- Digestive Health: The fiber content in both the leaves and fruits aids digestion and helps maintain healthy bowel movements.
- Medicinal Uses: In traditional African medicine, Gboma leaf eggplant is used to treat a variety of ailments, including stomach issues, inflammation, and skin conditions. The fruit’s bitterness is also believed to have digestive and liver health benefits.
Culinary Uses
- Leaves:
- The leaves are often boiled, sautéed, or used in soups and stews, similar to other leafy greens.
- Commonly prepared with palm oil, onions, tomatoes, and peppers in African cuisines.
- Popular dishes include Gboma leaf stew, often served with fufu or rice.
- Fruits:
- The fruits are typically cooked before consumption due to their bitterness when raw.
- Used in various sauces, stews, or eaten as a vegetable side dish.
- In some regions, the fruits are pickled or preserved.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.