Botanical Description
- Botanical Name: Lupinus hartwegii (Pixie Lupine)
- Common Name: Pixie Lupine, Dwarf Lupine
- Family: Fabaceae (Legume family)
- Origin: Native to North and Central America, bred for compact growth.
- Plant Type: Herbaceous annual or short-lived perennial
- Height: Typically 30-50 cm (12-20 inches)
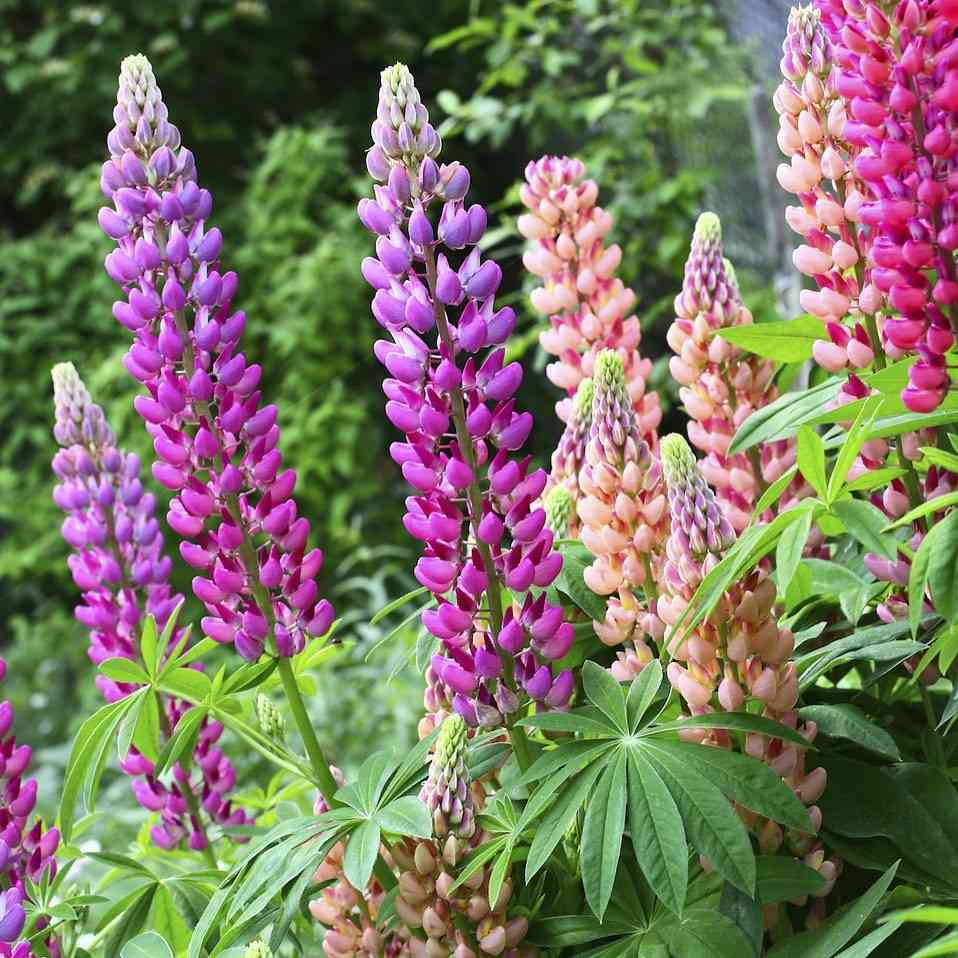
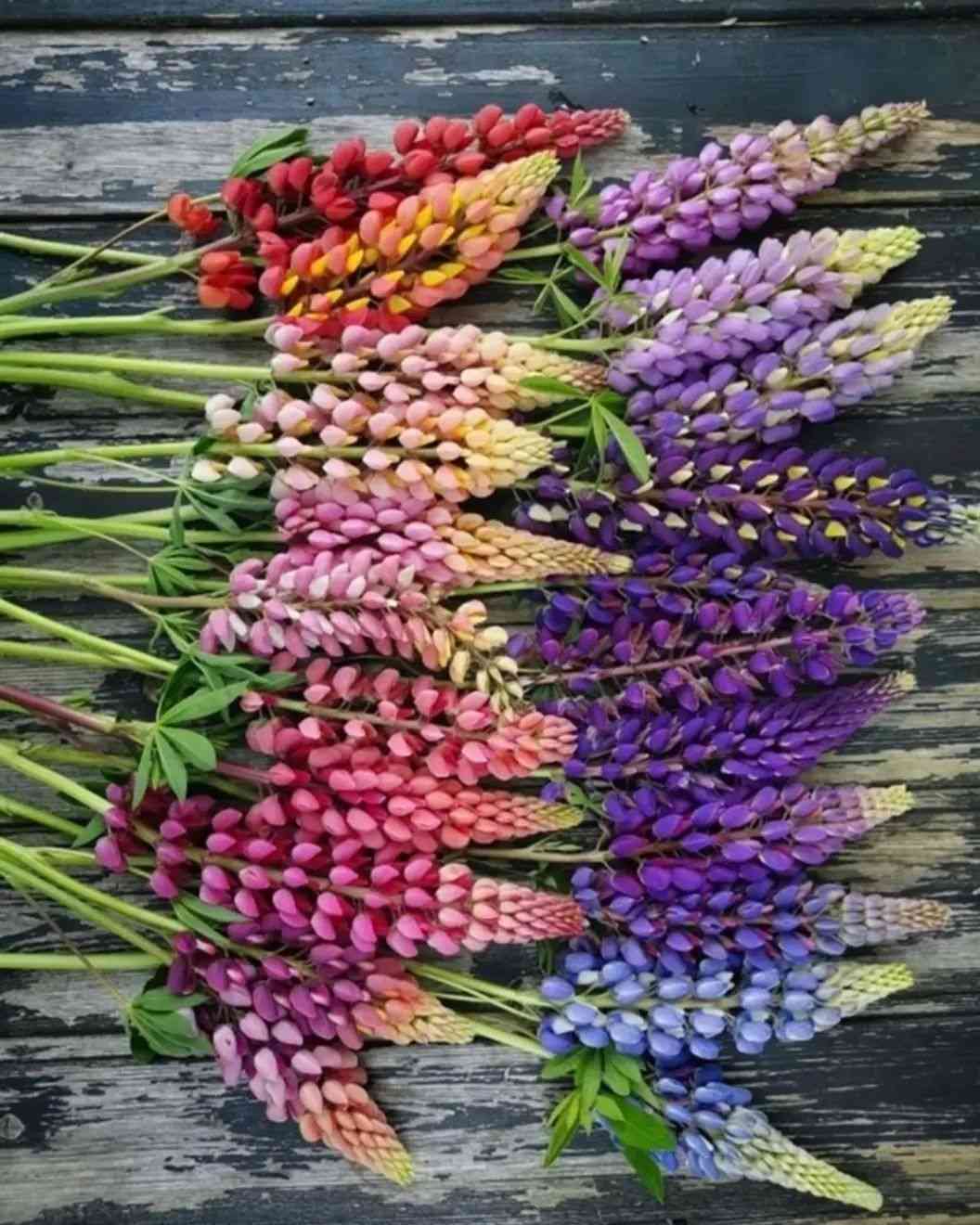
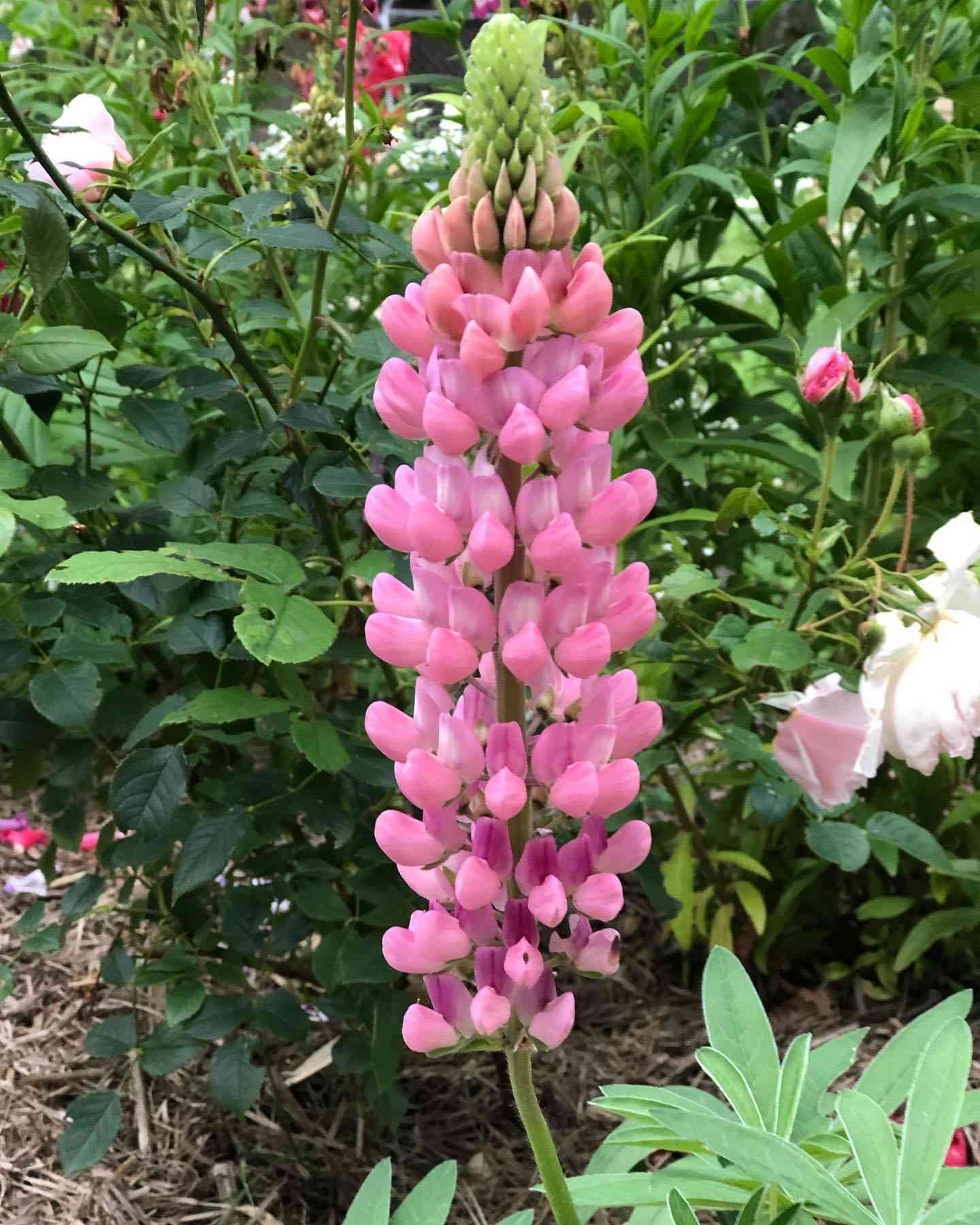
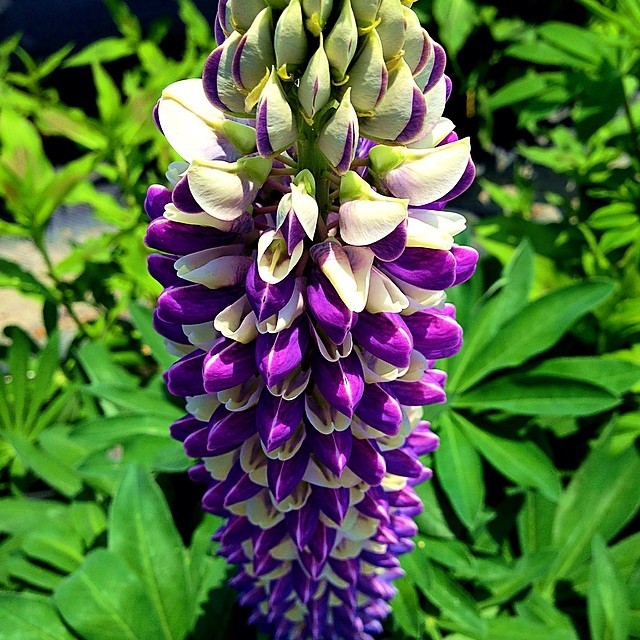
- Flower Structure: Dense, upright spikes of pea-like flowers in vibrant colors such as pink, purple, blue, yellow, and white.
- Leaf Structure: Palmately compound leaves with 7-10 narrow, elongated leaflets.
- Bloom Time: Late spring to early summer.
Growing Instructions for Lupin Pixie Mix:
- Sow Time: Sept to Nov is a good time to sow the seeds.
- Propagation: Lupins are grown from seeds, they should be scarified or soaked before planting to help with germination. They can also self-seed in some conditions.
- Soil: Well-draining, slightly acidic to neutral soil is ideal.
- Sunlight: Full sun or light shade.
- Spacing: Since they’re dwarf, space the plants about 15-20 cm apart.
- Watering: Keep the soil moist during the early stages but avoid overwatering.
Ecological Importance:
- Nitrogen Fixation: As legumes, lupins form symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in their roots. These bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use, enriching the soil. This makes lupins valuable in crop rotations or as a green manure crop.
- Pollinator Attraction: Lupins are very attractive to pollinators like bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. The bright colors and abundant nectar make them a favorite in pollinator-friendly gardens.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.